Real Time Food Tracking System | A Case Study of Amasi
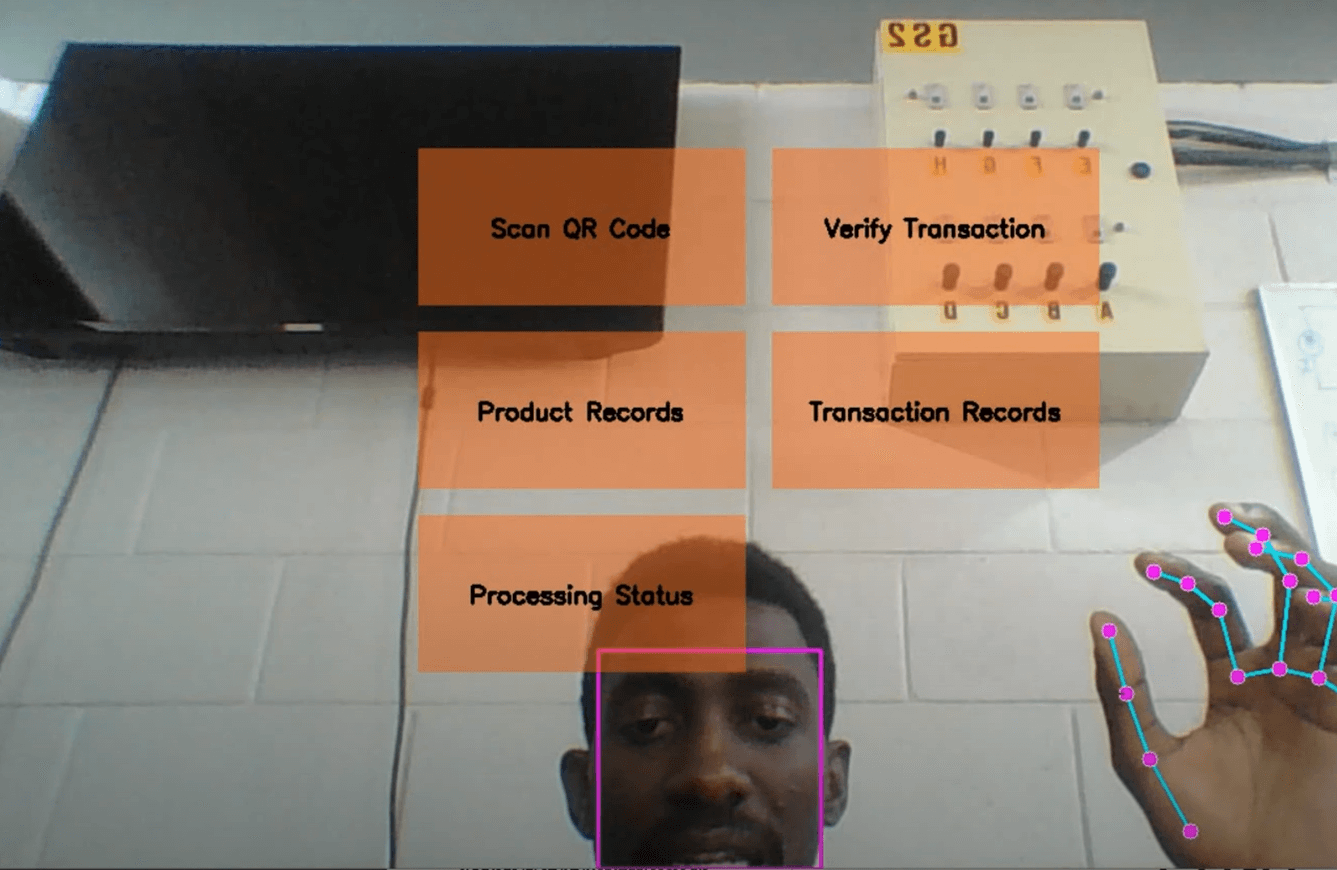
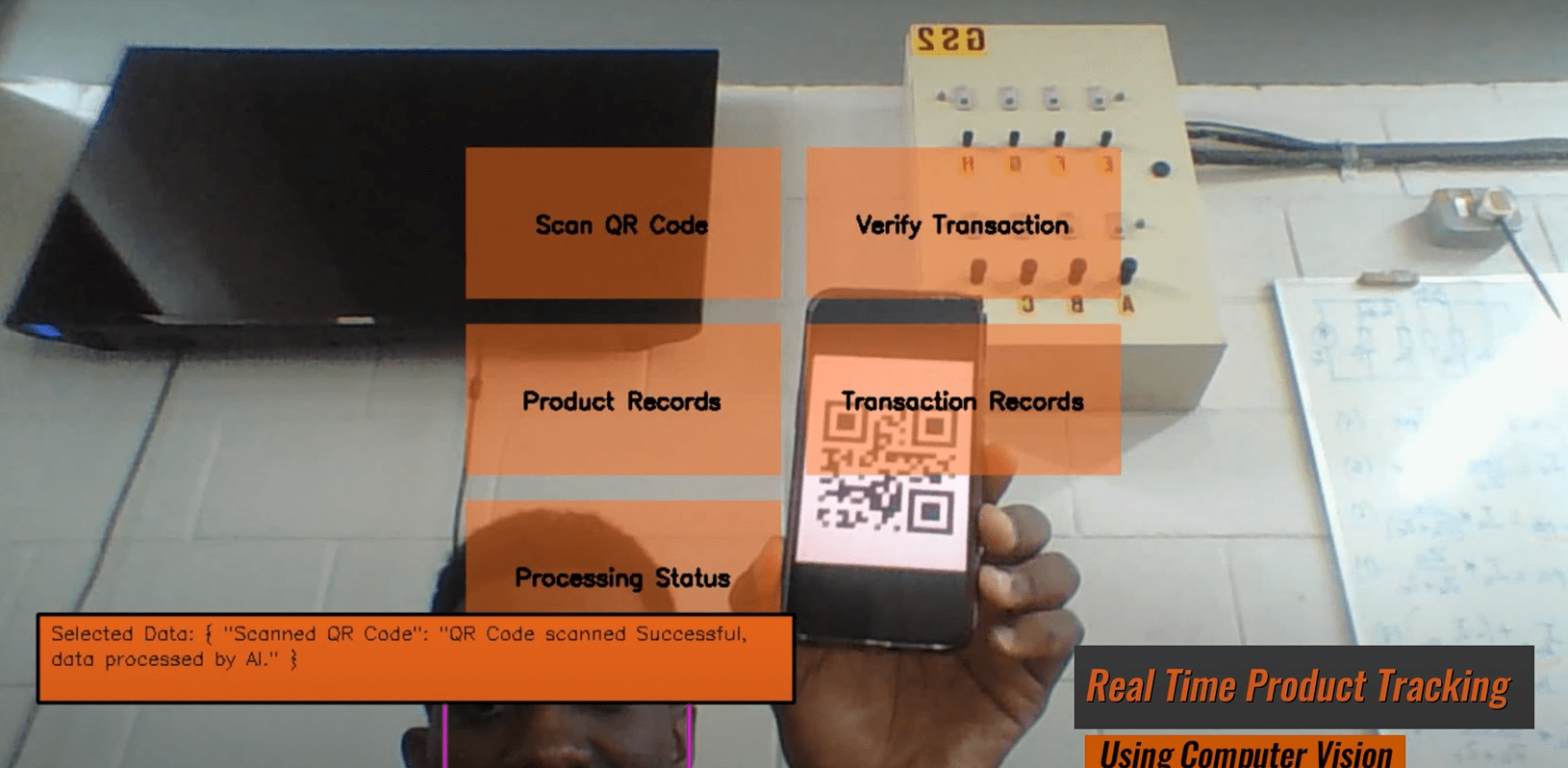
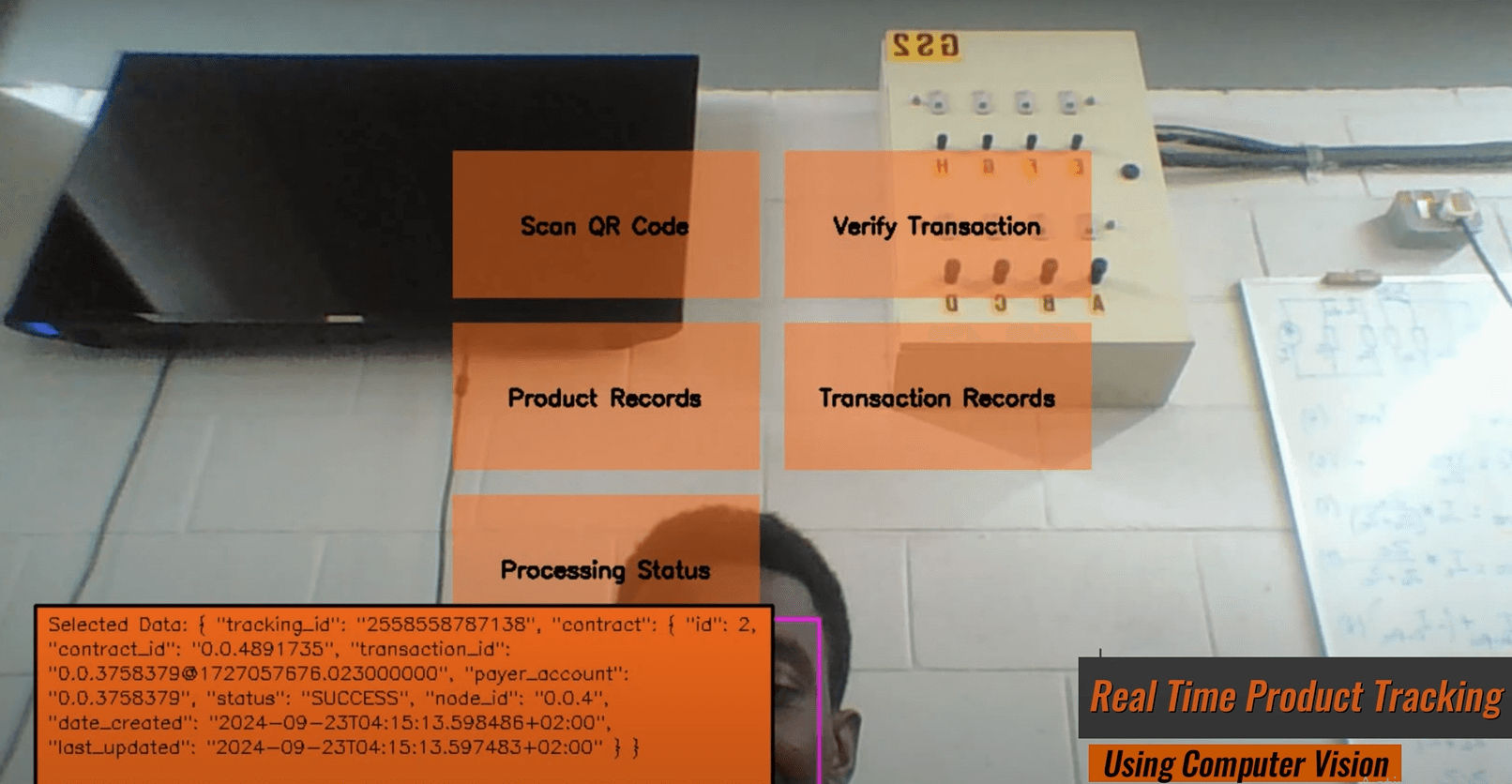
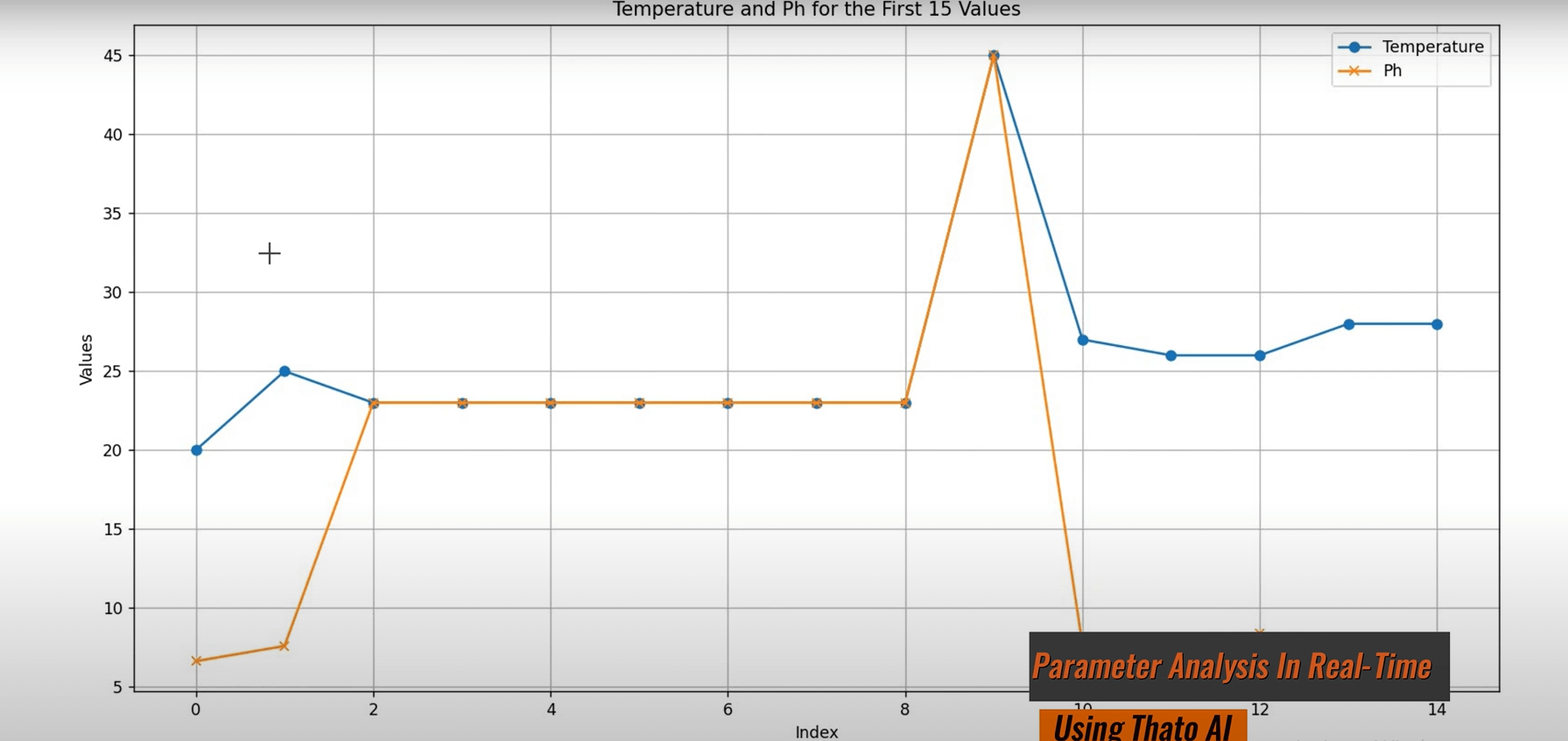
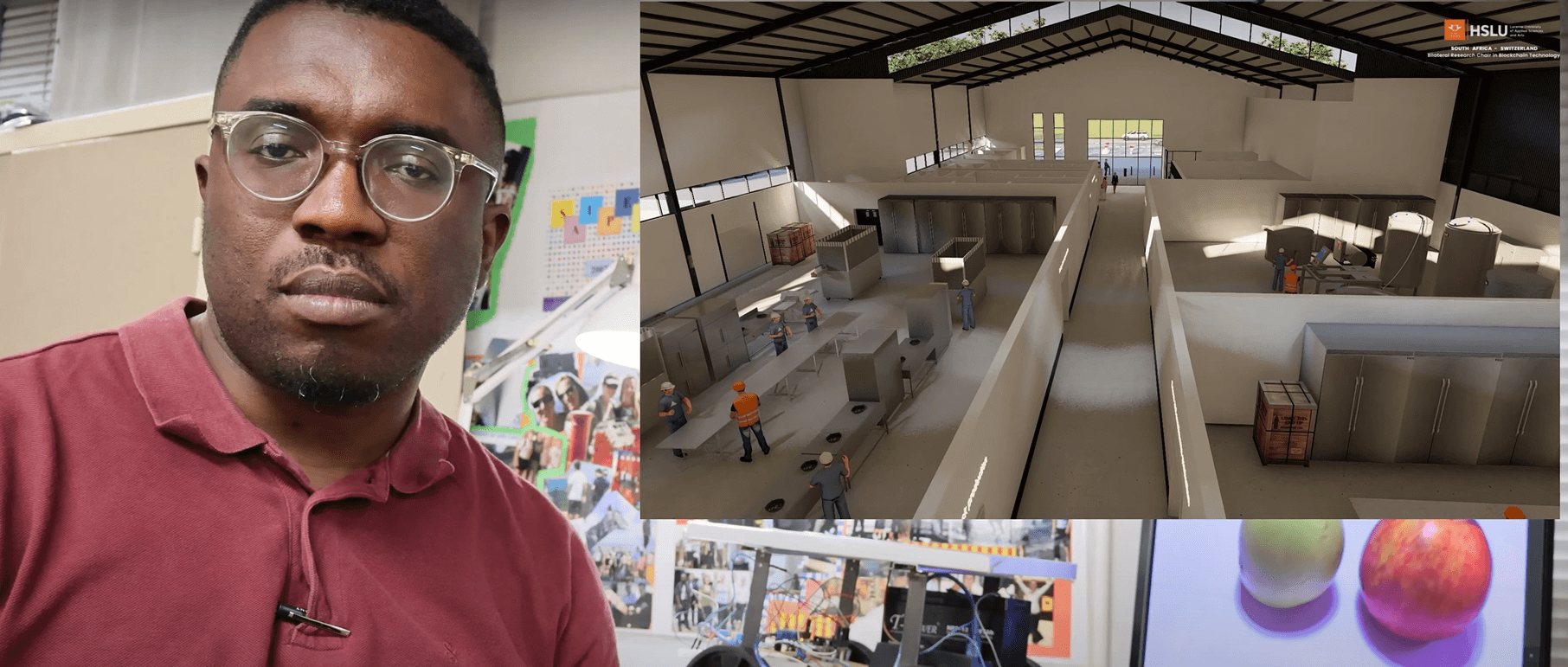
The Center for Cyber-Physical Food, Energy and Water Systems is leading the way in utilising Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) technologies to enhance the management of food, energy, and water resources. One of its groundbreaking initiatives is the development of a smart agro-processing facility that integrates machine learning, the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain technology, among other 4IR advancements. This facility is currently applied to the production of Amasi and Mahewu, traditional fermented beverages in South Africa. The smart agro-processing facility collects data on the fermentation process and securely stores it on a blockchain, allowing consumers to access this information via QR codes. This integration ensures food safety and facilitates market penetration for agro-processors.